INTRODUCTION
Kyowa Machining Oil has been researched and developed in order to increase the productivity for the manufacturer of high-precision, High-Tech industries such as the information industry, the office automation industry, the space, the medical appliances industry, the audio-visual industry.
Our products have been contributing greatly to our customers as their trusted brand for more than 20 years in Japanese high-tech industries. This has been possible because our customers benefit through
1) Shortening of machining time
2) Prolonged tool life
3) Minimization of down time since the oil always assure constant accuracy in micron order
We especially specialise in 'Hard-To-Machine' materials such as 13-Cr stainless steel, 18-8 stainless steel, Titan-alloy, Carbon steel, Copper alloy and Pure copper, etc.

You might not believe these features because they are too good to be true. However, we show you how our products work well.
FEATURES OF "MACHINING OIL"
1. Machining oil prolongs remarkably the tool's life from the damage by the built-up-edge and the heat.
2. Machining oil results in improved accuracy in machined surface and in reduced defective ratio.
3. Machining oil makes machining time much shorter and consequently increases output.
4. Machining oil set you free from "guide bush trouble".
5. Machining oil is added suitable additives based on the characteristic research of work piece so that each additive can properly
show its character.
6. Machining oil keep it effect much longer than other brand machining oil.
HOW SHOULD IT BE TO BE EFFECTIVE
A. Cutting Mechanism
1. Dynamics of metal cutting work (click for more)
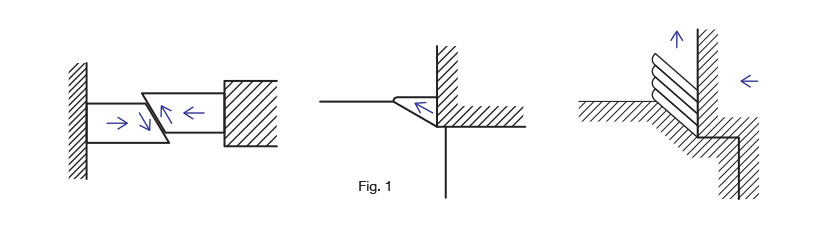
During metal working process, the shearing force of the tool acts on the base metal, taking off the chips like peeling an apple.
2. Generation of Heat (click for more)
A. Cutting Mechanism
1. Dynamics of metal cutting work
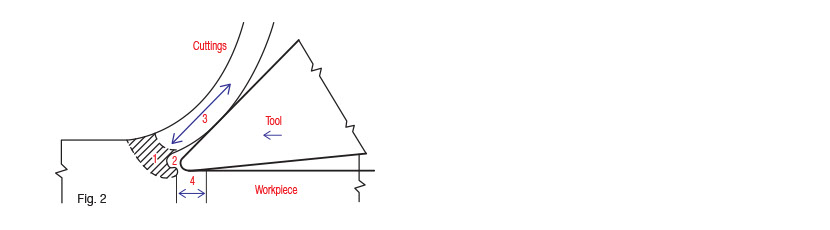
1. The first region of deformation
(by the shearing effect)
2. The second region of deformation
(by the built-up-edge)
3. The first region of sliding friction
(tool-cuttings)
4. The second region of sliding friction
(tool-work piece)
1-3% of the energy needed for cutting work remains inside the work piece & cutting (chips) as the residual stress, but more than 97% if the work energy turns into hear energy,
In Fig.2, the heat is generated at 1 & 2 by deformation, and next at 3 & 4 by sliding friction. These heats cause much trouble in metal cutting work such as damage to tools, variation of tolerance and difficulty of handling works.
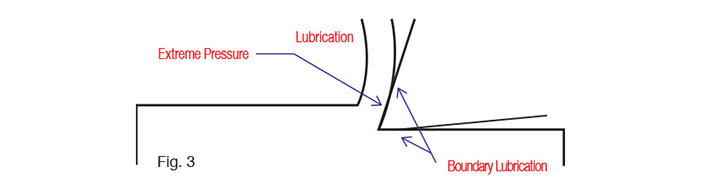
1. Boundary Lubrication
Under this condition, lubricating oil film becomes very thin and the thickness of molecular film stuck to the surface of metal becomes the same size as the molecule. Furthermore, both surfaces of metal touch and wear away each other.
2. Extreme Pressure Lubrication
Under the condition of Boundary Lubrication, if the pressure increases further, direct touch and friction repeatedly occur between both Metal. As a result of these movements, Boundary Lubricant film is destroyed because of the increase of heat and pressure. Therefore oil film is useless under this condition.
C. Function of Cutting Oil
Let's have a look at Fig. 3. In cutting work, we have only to know of which material works well under Boundary Lubricants and Extreme Pressure Lubrication.
1. Fatty oil works well under Boundary Lubrication!
At Boundary Lubrication, can find fatty oil work well. Free fatty acid or fatty acid in the fatty oil is absorbed to oxidized metal surface and makes metalic soap by reacting to oxidized metal film. This metallic soap reduces the sliding friction energy between work piece and tool. However, the fatty oil begins to burn (oxidize) when the cutting temperature gets over 200°c. That is to say that the fatty oil is useful for light duty cutting work and the improvement of machined face, but for the heavy duty cutting work the fatty oil is of no use and needs the help of the E.P.* (Extreme Pressure) additives.
2. Extreme Pressure additive gives you final solution!
f= s/p f: coefficient of friction
s: entropy p: load per unit area

If we can make 'S' smaller by means of transforming metal into Extreme Pressure film of low shearing force, we can reduce the sliding friction energy even in the small change of 'P'. The E.P. Lubrication territory, E.P. Additives react rapidly to the naked surface of metal with the partial climb of temperature and transform the metal into the metal of much lower shearing force which needs less work energy, We call the transformed metal E.P. film. This E.P. film works well in heavy duty cutting work.
There are three kinds of E.P. Additives; Chlorinated E.P. Additives, Sulpherised E.P. Additive and Phospho rated E.P. Additive. We do not use Phosphorated E.P. Additives for cutting oil because we are not sure of its effect against the built-up-edge and also not sure about the influence on human's health. We use Chlorinated E.P. Additive and Sulpherised E.P. Additive, solely or together. At the chip/tool interface, the temperature rises until approx. 800°c depending on its condition. Chlorinated E.P. Additive starts to cause dechlorination at the point of approx. 250°c and causes rust problem. Sulpherised E.P. Additive starts its reaction around 200°c and works well until approx. 800°c. However, this additive is not so active at the low temperature, so we usually use them together.
The above mentioned theory is a rough explanation, but our products can prove this theory true. We provide minutely subdivided products according to the cutting conditions and the work materials for our customers. We can even adjust our products to the customers' demands.
Please consult our sales engineer for details.
@ COPYRIGHT BY KYOWA PETROCHEMISTRY 2017